Translations:Einzugsgebiet/36/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Ferrao (Diskussion | Beiträge) (Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „As a result, the value C ranges between 0.8 < C < 0.9. This ensures that different rainfall indices are calculated for the same amount of rainfall at different…“) |
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
As a result, the value C ranges between 0.8 < C < 0.9. This ensures that different rainfall indices are calculated for the same amount of rainfall at different times of the year | As a result, the value of C ranges between 0.8 < C < 0.9. This ensures that different rainfall indices are calculated for the same amount of rainfall at different times of the year, thus taking into account different degrees of runoff readiness. | ||
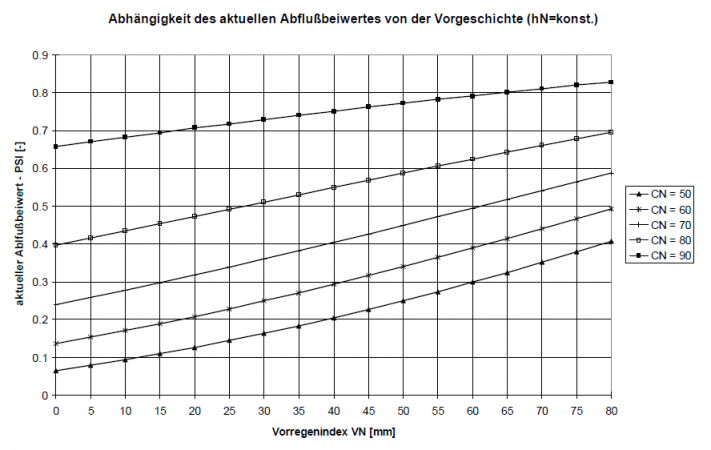
Depending on the | Depending on the previous conditions quantified in this way, a current discharge coefficient can be calculated using the CN values specific to the area and valid for average previous conditions. The following figure shows how the current discharge coefficient for different CN-values changes depending on previous conditions. | ||
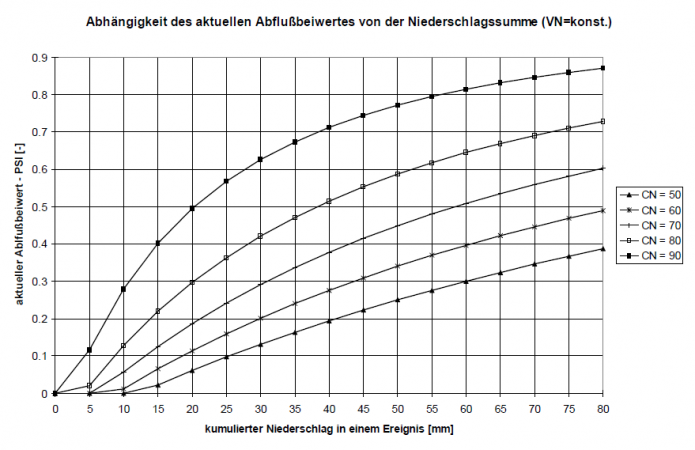
Since the runoff readiness of a catchment area changes | Since the runoff readiness of a catchment area changes during the course of a rainfall event due to soil moistening, the runoff coefficient is also adjusted during an event as a function of the cumulative precipitation amount. | ||
<gallery mode="packed" heights=300px> | <gallery mode="packed" heights=300px> | ||
Datei:Abhängigkeit_des_Abflussbeiwertes_von_der_Vorgeschichte.png|Dependence of the | Datei:Abhängigkeit_des_Abflussbeiwertes_von_der_Vorgeschichte.png|Dependence of the runoff coefficient on previous conditions | ||
Datei:Abhängigkeit_des_Abflussbeiwertes_von_der_kumulierten_Niederschlagssumme.png|Dependence of the runoff coefficient on the cumulative precipitation sum | Datei:Abhängigkeit_des_Abflussbeiwertes_von_der_kumulierten_Niederschlagssumme.png|Dependence of the runoff coefficient on the cumulative precipitation sum | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Version vom 25. November 2020, 11:39 Uhr
As a result, the value of C ranges between 0.8 < C < 0.9. This ensures that different rainfall indices are calculated for the same amount of rainfall at different times of the year, thus taking into account different degrees of runoff readiness. Depending on the previous conditions quantified in this way, a current discharge coefficient can be calculated using the CN values specific to the area and valid for average previous conditions. The following figure shows how the current discharge coefficient for different CN-values changes depending on previous conditions. Since the runoff readiness of a catchment area changes during the course of a rainfall event due to soil moistening, the runoff coefficient is also adjusted during an event as a function of the cumulative precipitation amount.