Speicher/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| Zeile 114: | Zeile 114: | ||
An addition of water caused by precipitation onto the reservoir's surface or losses caused by evaporation or infiltration can be considered via two options: | An addition of water caused by precipitation onto the reservoir's surface or losses caused by evaporation or infiltration can be considered via two options: | ||
* Constant | * Constant hydrograph (daily, weekly and/or annual pattern) | ||
* Time series | * Time series | ||
These can be scaled by a factor. | These can be scaled by a factor. | ||
The reservoir loss/contribution is additionally scaled automatically with the current storage surface | The reservoir loss/contribution is additionally scaled automatically with the current storage surface | ||
Version vom 26. November 2020, 15:11 Uhr
Reservoirs are used to store an inflow and, depending on the current storage content and operating rules, to release water for different uses to up to three different system elements. With the possibility to regulate and control releases, it is an extremely flexible system element with a variety of options. Originally, the reservoir was developed to represent reservoirs behind dams, but it can also be used to model other reservoirs such as flood control reservoirs or similar. Additionally, it is possible to optionally simulate the addition of water to the reservoir by precipitation, as well as losses from the reservoir by evaporation and infiltration.
The reservoir system element can also be used to simulate hydro power plants.
Rating Curve
The reservoir rating curve defines the relationship between storage volume, water level and surface area. It forms the basis for all calculation options that depend on not only the storage volume but also the water level and/or the surface area e.g., precipitation/losses, flow over a weir, pressurized flow through pipes.
Releases
The term release is used to describe any discharge of water according to operating rules from the reservoir to the downstream area through regulated or unregulated outlets. This includes controlled releases through operating and bottom outlets as well as releases via a spillway.
Releases are often related to operating rules, therefore, it is possible or sometimes also necessary to define several releases for each outlet.
Calculation Options
Independent of the selected calculation option, releases can always be scaled with a system state/control cluster, which makes it possible to model complex operating rules, which are not only dependent on states within the reservoir, but also on other states within the river basin.
Release per Timestep / Release Sequence
With this option, you define the release values by directly entering (up to 365) values. During the simulation, these values are then used as release values for the individual simulation timesteps in the given order.
Function (+ Hydrograph/Time Series)
With this option, releases are defined as functions of storage volume by entering the nodes of the function. These releases can additionally be scaled with a factor, an annual, weekly and/or daily pattern (and, as with all calculation options, with a system state or a control cluster) or with a factor and a time series.
The following function types are available:
|
KNL |
Kennlinie |
|
LAM |
Lamellenplan |
|
XYZ |
Zeitabhängige Funktion |
Rating Curve
The rating curve consists of a time-independent functional relationship between releases and storage volume. You can specify whether the function should be interpolated linearly between the entered nodes or whether the function should be interpreted as a step function.
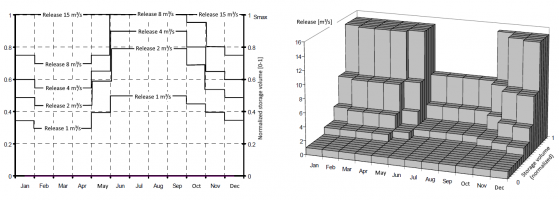
Pool-Based Operating Plan
With the option pool-based operating plan, the reservoir storage is divided into different pools which vary over the year and these pools are each assigned a fixed release amount. A pool-based operating plan is defined by entering a number of releases with ascending amounts and specifying the corresponding storage volume for each release amount at different times of the year.
The areas between the entered nodes can be interpreted as steps. However, it is also possible to interpolate linearly in time and/or between the release amounts.
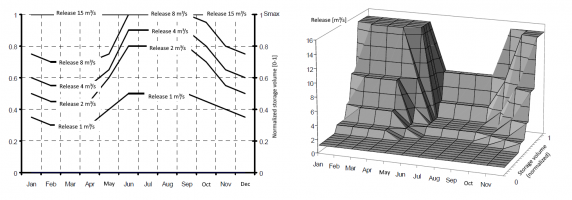
Time-Dependent Function
A time-dependent function is very similar to a pool-based operating plan, but a bit more flexible: the releases defined at different time periods only have to be of equal number but not in value, and they do not necessarily have to be ascending. This makes it possible to define arbitrary functions with individual nodes for release amounts and storage volumes for different time periods.
By default the functions are interpreted as steps with constant values between the entered nodes. However, it is also possible to interpolate linearly in time and/or between the entered storage-release value pairs.
Weir Overflow
The release is calculated using the weir formula according to Poleni as free / submerged overflow.
Pressure Pipeline
The release is calculated according to the Prandtl-Colebrook and Darcy-Weisbach formulas.
Turbine
Based on the characteristics of the turbine, the flow through the turbine is determined depending on the storage level and the downstream water level, such that the desired power output is maintained as long as the maximum possible flow rate of the outlet is not exceeded. See also the page on hydropower plants.
Limits
The maximum physically possible output of individual outlets can be entered as functions of storage volume, causing releases to be limited to these values. It is also possible to specify a minimum permissible release value, below which the release will be set to 0.
Internal Dependencies
Internal dependencies are used to define the priorities in case of multiple competing releases from one reservoir. One or more releases can be reduced if another release exceeds a certain amount or if the storage volume falls below a certain value.
The limits for releases and storage volumes for internal dependencies are entered as constant values, which can however be scaled with daily, weekly and/or annual patterns.
If several charges are reduced, the order in which they are to be reduced must also be specified.
Example: If release B > 0 and the storage volume S < X, then reduce release A by the amount of release B, but at most to a minimum value of zero.
This means that there is a linear relatioship between A and B until B is equal to the value of A. If the value of B rises any further, A still remains zero.
Precipitation/Losses
An addition of water caused by precipitation onto the reservoir's surface or losses caused by evaporation or infiltration can be considered via two options:
- Constant hydrograph (daily, weekly and/or annual pattern)
- Time series
These can be scaled by a factor. The reservoir loss/contribution is additionally scaled automatically with the current storage surface